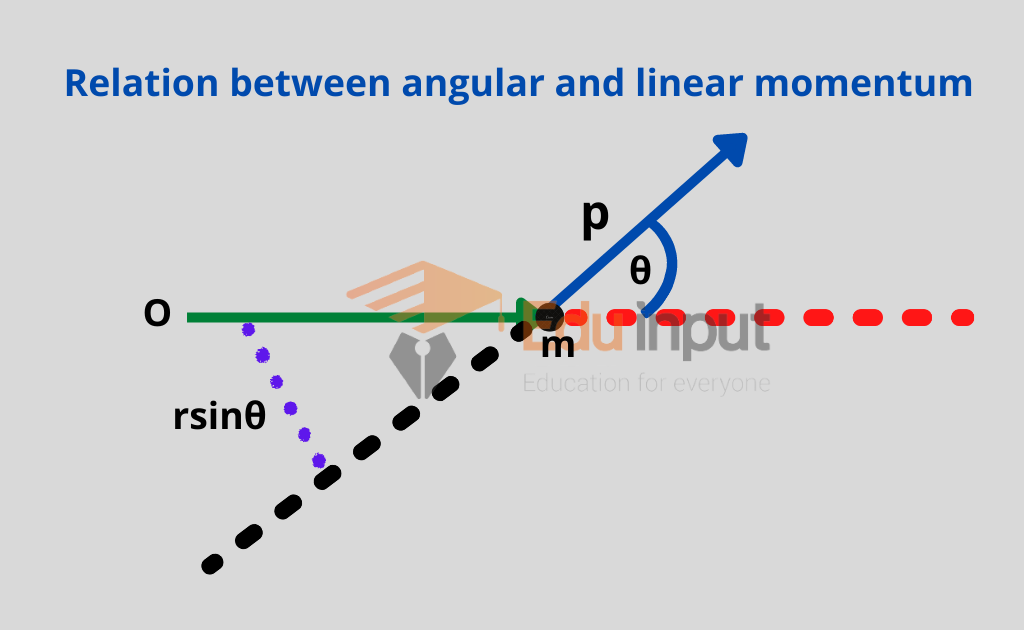
Linear Vs Angular Momentum . the main idea. the angular momentum of a single particle about a designated origin is the vector product of the position vector in. since linear momentum is equal to mass times linear velocity, we can make an educated guess that angular momentum is equal to rotational inertia times. linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight line, while angular momentum refers to the motion of an. Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has some more. we have a definition for the angular momentum of a rigid object, but can we define the angular momentum of a. linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object in motion, while angular momentum is the rotational equivalent,.
from eduinput.com
since linear momentum is equal to mass times linear velocity, we can make an educated guess that angular momentum is equal to rotational inertia times. linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight line, while angular momentum refers to the motion of an. linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object in motion, while angular momentum is the rotational equivalent,. Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has some more. the angular momentum of a single particle about a designated origin is the vector product of the position vector in. the main idea. we have a definition for the angular momentum of a rigid object, but can we define the angular momentum of a.
Angular Momentum Law of Conservation of Angular Momentum
Linear Vs Angular Momentum since linear momentum is equal to mass times linear velocity, we can make an educated guess that angular momentum is equal to rotational inertia times. the angular momentum of a single particle about a designated origin is the vector product of the position vector in. linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object in motion, while angular momentum is the rotational equivalent,. Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has some more. linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight line, while angular momentum refers to the motion of an. the main idea. since linear momentum is equal to mass times linear velocity, we can make an educated guess that angular momentum is equal to rotational inertia times. we have a definition for the angular momentum of a rigid object, but can we define the angular momentum of a.
From www.youtube.com
Angular Momentum of Objects in Linear Motion YouTube Linear Vs Angular Momentum we have a definition for the angular momentum of a rigid object, but can we define the angular momentum of a. the angular momentum of a single particle about a designated origin is the vector product of the position vector in. Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has some more. linear momentum refers. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT LINEAR AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM, PRINCIPLE OF IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM PowerPoint Presentation Linear Vs Angular Momentum linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object in motion, while angular momentum is the rotational equivalent,. Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has some more. the main idea. linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight line, while angular momentum refers to the motion. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From www.youtube.com
angular momentum l geometrical interpretation l linear momentum l cross product l areal velocity Linear Vs Angular Momentum linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object in motion, while angular momentum is the rotational equivalent,. linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight line, while angular momentum refers to the motion of an. Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has some more. the. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From physicskhleifat.weebly.com
Unit 6 Rotational Motion SAMI KHLEIFAT AP PHYSICS 1 Linear Vs Angular Momentum linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object in motion, while angular momentum is the rotational equivalent,. since linear momentum is equal to mass times linear velocity, we can make an educated guess that angular momentum is equal to rotational inertia times. the main idea. we have a definition for the angular. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From www.difference.wiki
Linear Momentum vs. Angular Momentum What’s the Difference? Linear Vs Angular Momentum Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has some more. the angular momentum of a single particle about a designated origin is the vector product of the position vector in. linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight line, while angular momentum refers to the motion of an. the main. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Angular Momentum PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5286371 Linear Vs Angular Momentum we have a definition for the angular momentum of a rigid object, but can we define the angular momentum of a. linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object in motion, while angular momentum is the rotational equivalent,. Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has some more. since linear. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From www.youtube.com
Solid Mechanics Theory Balance of Linear and Angular Momentum YouTube Linear Vs Angular Momentum since linear momentum is equal to mass times linear velocity, we can make an educated guess that angular momentum is equal to rotational inertia times. linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight line, while angular momentum refers to the motion of an. the main idea. the angular momentum of a single. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From eduinput.com
Angular Momentum Law of Conservation of Angular Momentum Linear Vs Angular Momentum we have a definition for the angular momentum of a rigid object, but can we define the angular momentum of a. Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has some more. linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight line, while angular momentum refers to the motion of an. the. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From study.com
Angular Momentum vs. Linear Momentum Lesson Linear Vs Angular Momentum the angular momentum of a single particle about a designated origin is the vector product of the position vector in. the main idea. Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has some more. linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object in motion, while angular momentum is the rotational equivalent,.. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From www.differencebetween.com
Difference Between Linear Momentum and Angular Momentum Compare the Difference Between Similar Linear Vs Angular Momentum since linear momentum is equal to mass times linear velocity, we can make an educated guess that angular momentum is equal to rotational inertia times. linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight line, while angular momentum refers to the motion of an. Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From studybrewmaster.z21.web.core.windows.net
Why Is Angular Momentum Conserved Linear Vs Angular Momentum linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight line, while angular momentum refers to the motion of an. we have a definition for the angular momentum of a rigid object, but can we define the angular momentum of a. Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has some more. since. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Physics 1901 (Advanced) PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4437085 Linear Vs Angular Momentum Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has some more. we have a definition for the angular momentum of a rigid object, but can we define the angular momentum of a. linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight line, while angular momentum refers to the motion of an. the. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Angular momentum in quantum mechanics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5405719 Linear Vs Angular Momentum the angular momentum of a single particle about a designated origin is the vector product of the position vector in. since linear momentum is equal to mass times linear velocity, we can make an educated guess that angular momentum is equal to rotational inertia times. linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From byjus.com
what are angular and linear momentum Linear Vs Angular Momentum the angular momentum of a single particle about a designated origin is the vector product of the position vector in. the main idea. Linear momentum tends to behave fairly intuitively, but angular momentum has some more. we have a definition for the angular momentum of a rigid object, but can we define the angular momentum of a.. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From www.youtube.com
Angular momentum Basic & angular momentum for linear, circular & rotational motion YouTube Linear Vs Angular Momentum the angular momentum of a single particle about a designated origin is the vector product of the position vector in. linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object in motion, while angular momentum is the rotational equivalent,. since linear momentum is equal to mass times linear velocity, we can make an educated guess. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Physics 101 Lecture 16 Angular Momentum PowerPoint Presentation ID9578768 Linear Vs Angular Momentum since linear momentum is equal to mass times linear velocity, we can make an educated guess that angular momentum is equal to rotational inertia times. the main idea. linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object in motion, while angular momentum is the rotational equivalent,. we have a definition for the angular. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Tutorial 12 Linear Momentum Angular Momentum PowerPoint Presentation ID647481 Linear Vs Angular Momentum linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object in motion, while angular momentum is the rotational equivalent,. the main idea. linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight line, while angular momentum refers to the motion of an. the angular momentum of a single particle about a designated. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.
From www.youtube.com
Angular Momentum Linear Momentum vs Angular Momentum Class 11th Physics in Hindi YouTube Linear Vs Angular Momentum the main idea. linear momentum refers to the motion of an object in a straight line, while angular momentum refers to the motion of an. since linear momentum is equal to mass times linear velocity, we can make an educated guess that angular momentum is equal to rotational inertia times. the angular momentum of a single. Linear Vs Angular Momentum.